The men came at Hope and her baby with spears and guns. But she would not leave. There was no place for her to go.
When the air-gun pellets pierced Hope’s eyes, blinding her, she felt her way up the tree trunks, auburn-furred fingers searching out tropical fruit for sustenance.
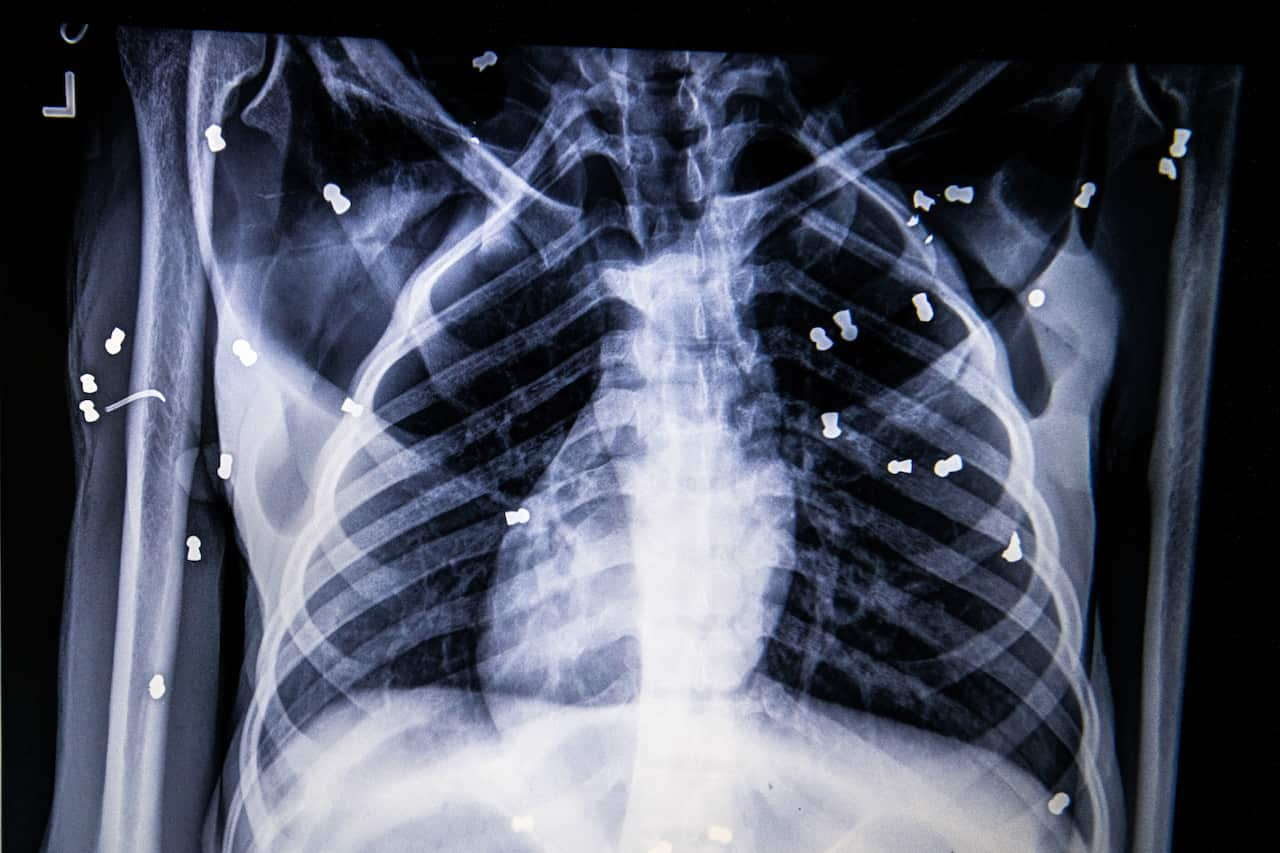
By the end, Hope’s torso was slashed with deep lacerations. Multiple bones were broken. Seventy-four pellets were lodged in her body. Her months-old baby had been ripped away.
Hope, who was named at a rehabilitation centre, is a Sumatran orangutan — a critically endangered animal that scientists warn could be the first major great ape species to go extinct. As jungle and swamp are cleared for palm oil plantations, orangutans, whose name means “people of the forest” in Malay, are losing the very habitat that gives them their identity.
All around the Indonesian island of Sumatra, charred landscapes of blackened tree stumps and singed earth attest to the devastation wrought by humans.
“Twenty thousand hectares are cleared and a couple trees are left and the orangutan looks around and says, ‘What happened to my forest?’” said Ian Singleton, the director of the Sumatran Orangutan Conservation Program.
Two nations, Indonesia and Malaysia, provide the world with more than 80 per cent of the palm oil used in everything from biofuel and cooking oil to lipstick and chocolate. Last September, amid concerns over diminishing habitat for endangered species and dangerous carbon emissions from mass burnings to clear land, Indonesia stopped issuing new licenses for palm oil plantations.
But as Hope’s plight shows, directives issued in air-conditioned government offices can mean little in poor villages. The global appetite for palm oil is still voracious.
“They say there is a moratorium, but I can see with my own eyes that land is being lost every day,” said Krisna, a coordinator for the Human Orangutan Conflict Response Unit, a group based on Sumatra that has rescued more than 170 injured orangutans since 2012. (Like many Indonesians, Krisna goes by a single name.)
Orangutans live on just two islands in the world. Apart from humans, they are the only great ape species that resides outside of Africa.
From 1999 to 2015, the orangutan population on the island of Borneo declined by more than 100,000, researchers reported in Current Biology, a scientific journal. There are about 100,000 orangutans remaining on Borneo, according to the World Wildlife Fund. On Sumatra — where more than half of the forest cover has been lost since 1985, according to a coalition of environmental groups called Eyes on the Earth — there are now fewer than 14,000 Sumatran orangutans.
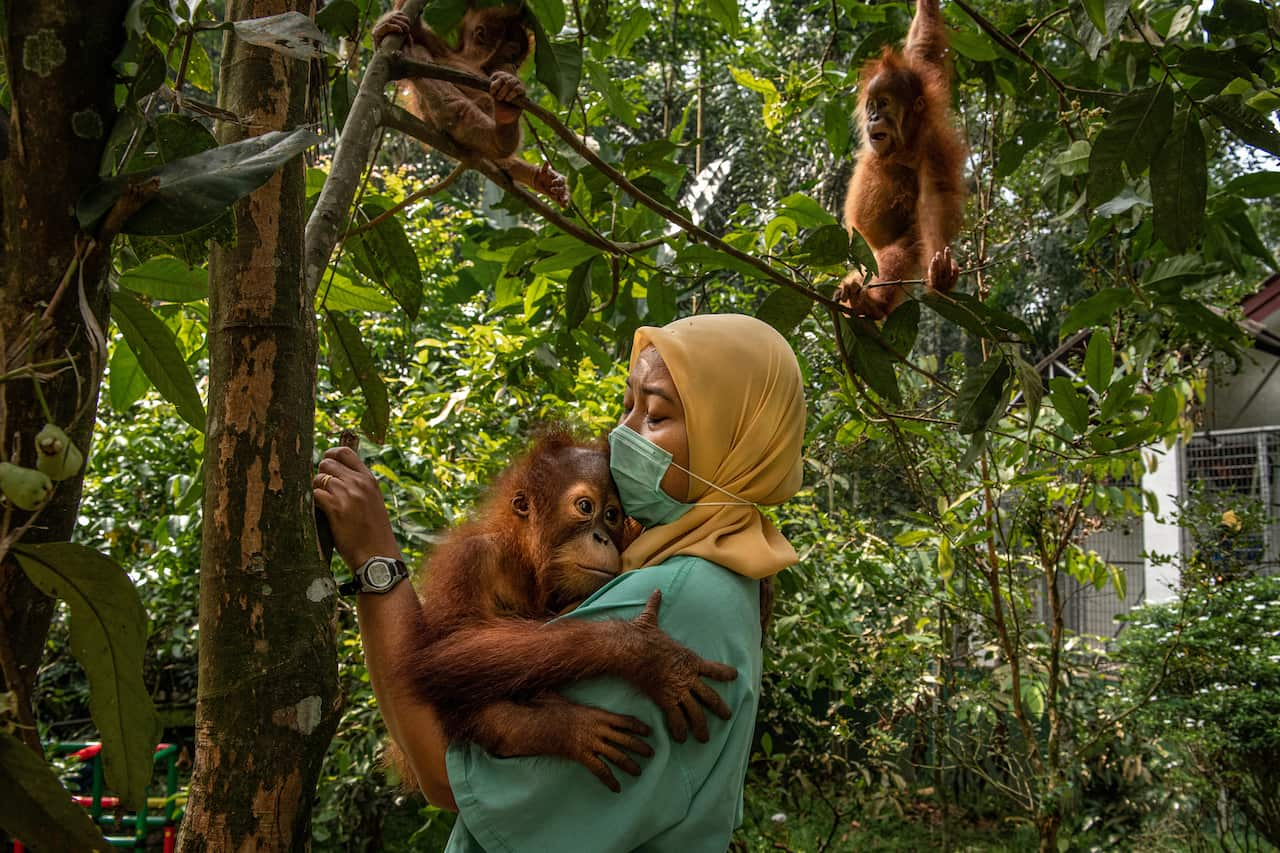

That might not sound like a figure heralding certain extinction. But because orangutan mothers let so much time pass between births — eight to nine years are dedicated to raising each child — scientists fear that the population is in a death spiral.
The unluckiest orangutans die in the fires set to clear the land. The more fortunate are marooned on small islands of trees among oil palms. Desperate for food, they stray into areas inhabited by humans, raiding crops and provoking villagers to act.
“They eat a couple fruit, and they get shot,” Singleton said. “And nothing’s done about it. There’s no law enforcement.”
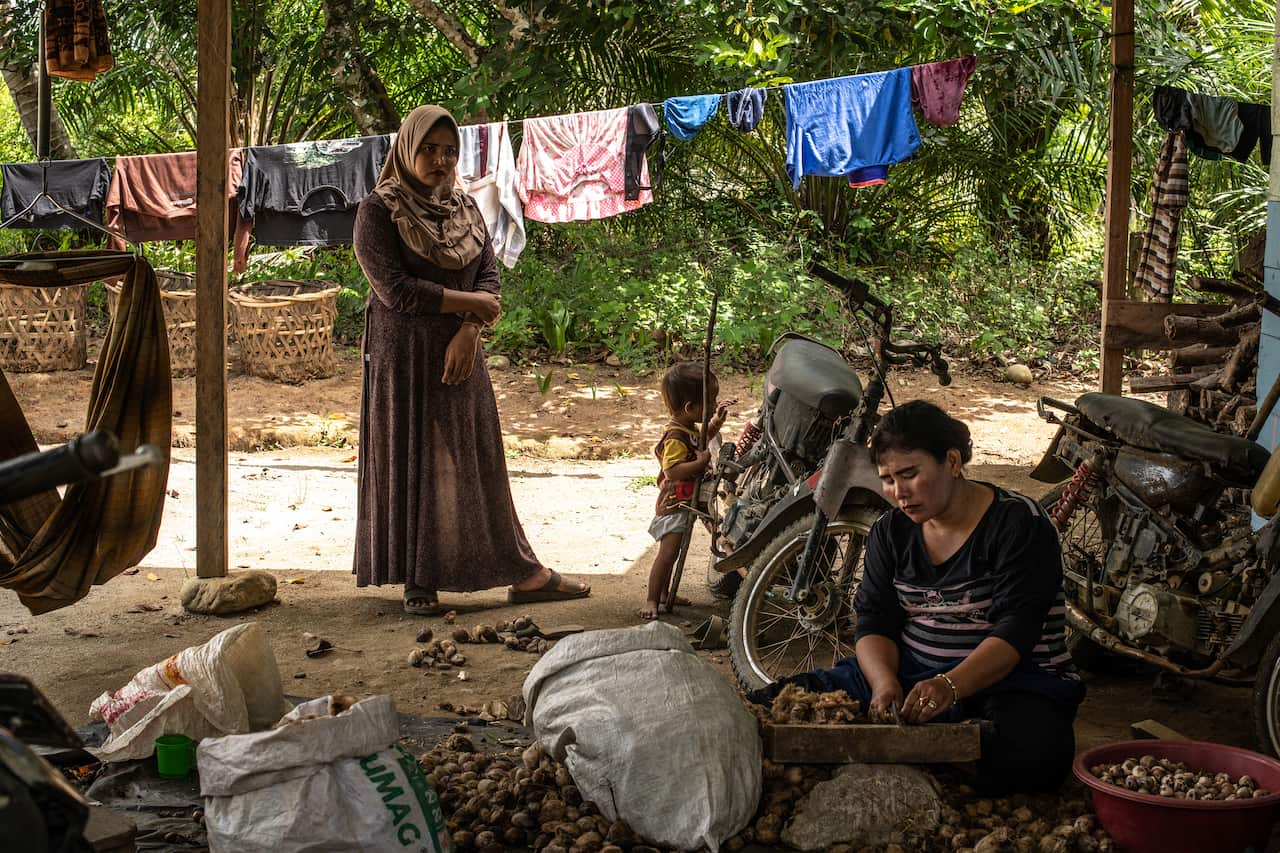
When Hope showed up earlier this year on the outskirts of Bunga Tanjung village in Aceh province on Sumatra, some of the earth was still smouldering. Neat rows of oil palm seedlings stretched toward the horizon. Confined to a narrow strip of secondary forest, Hope gobbled fruit from village orchards to survive.
The majority of Bunga Tanjung’s residents are not from Aceh, but are poor, economic migrants from other parts of Indonesia, lured by the demand for palm oil.
The palms, a species native to West Africa, provide essential income for often struggling farmers, even if the plants spread pernicious roots that make it difficult to till the land again.
“Without palm oil, we cannot survive,” said Sanita, the mayor of a Bunga Tanjung borough.

Over a period of weeks, villagers repeatedly shot at Hope, trying to scare her away. But with few places to go but the sliver of jungle, Hope stayed put.
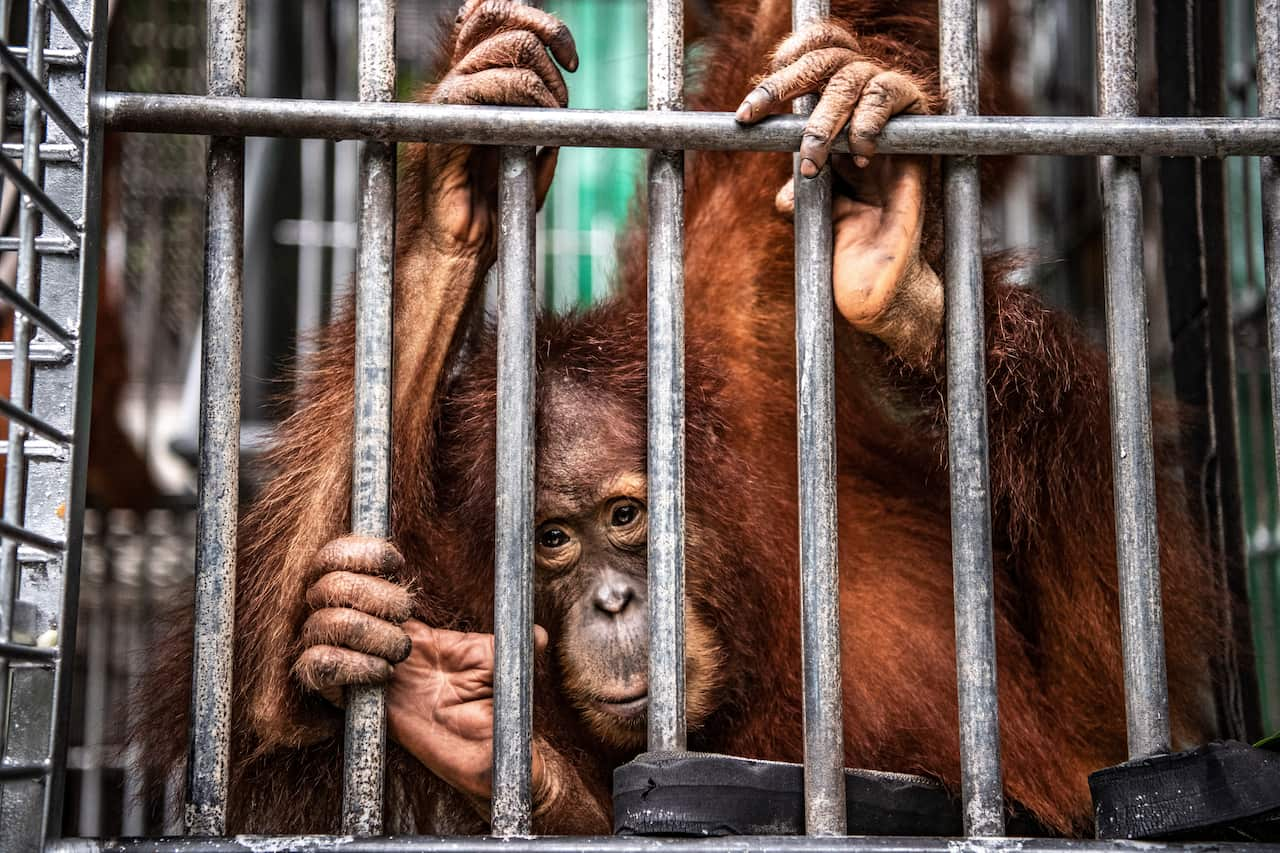
A 100-pound orange ape is considered an oversized pest, but Hope’s baby held promise for some in the village. Although selling endangered species is illegal, orangutan babies are often captured for the pet trade, or for zoos in need of a star attraction.
Compared to humans or chimpanzees, orangutans are the introverts of the ape world, leading largely solitary lives. But in captivity, they have been taught sign language, and their eye contact is disarming. Their exuberant smooching noises sound suspiciously like flirting.
A big-eyed baby with tufts of coppery hair can earn villagers $70 ($100AUD), according to local conservationists who have tracked the endangered species trade. By the time the apes are sold to unscrupulous zoos or private owners, they can go for 100 times that.
Adulthood, though, devalues the captive orangutans. They aren’t as cute. They are too strong. And few people have the time and energy to devote to such intelligent creatures, leaving many forgotten behind bars, their limbs and minds atrophied.
“We wouldn’t put a human in a cage so small they couldn’t turn around,” said Harista, a keeper at a rescue centre, who once taught an orangutan to swing on his arms again after 17 years of confinement. “Why do we do this to orangutans?”

In March, a teenager from Bunga Tanjung headed for a cluster of trees. His aim: To pry Hope’s baby from her arms. Even though pellets had robbed the mother of her eyesight, Hope struggled to protect her child, leaving scratches on the boy’s arms.
But the teenager did ultimately succeed in taking the baby away, keeping it in a basket outside his home.
By the time local forestry officials were alerted to Hope’s presence and mounted a rescue effort, the baby was barely responsive, said Krisna, the coordinator for the orangutan rescue organisation.
Sanita, the mayor, presented a different version of events. Hope was only in the village for a couple of days, he said, contradicting the evidence of weeks of orangutan nests built in nearby trees. No one in his village had shot her, he said, discounting the 74 pellets.
“We wouldn’t do anything to hurt orangutans, even though the orangutans bother us,” he said.
Sanita said he had no idea a baby was involved, although he later amended his story. If anyone had kidnapped a baby orangutan, he said, it would have been children.
“Adults know that taking an orangutan is illegal, so I’m sure no one in the village would do that,” he said. “Maybe it was just children playing around.”
With Hope sedated in the back of a vehicle, the baby restored to her embrace, Krisna rushed to Singleton’s rehabilitation centre near the city of Medan, 10 hours away.
The baby died along the way.
A Swiss surgeon flew out to operate on Hope. (Surgeons tend to be more adept than veterinarians at ape surgery.)
Hope is now recovering in an enclosure. She has learned through touch to accept a papaya or bottle of milk from a keeper.

Nearby, orphaned orangutans whimper and squeak. When Hope hears the babies, she curls into a foetal position and cries out.
Orangutans share nearly 97 per cent of their DNA sequence with humans. The remaining 3 per cent do not preclude Hope from mourning her baby. Her body is still producing milk.
“Hope’s body was broken, she lost her vision and her baby, and now she’s a wild animal in a cage,” said Yenny Saraswati, a veterinarian at the centre. “I can’t think of a more stressful situation.”
Back in Bunga Tanjung, Hope’s shadow lingers. The teenager, whose name is being withheld because he is a minor, has been questioned by the police, but because he’s underage it’s not clear whether he will be charged. No adults have come forward to claim responsibility for Hope’s many injuries.
The teenager has given up his dream of becoming a mechanic and rarely comes home now, according to his father, Aliong Sitepu. “He’s always in a bad mood,” Aliong said. “I don’t know how to talk to him.”
Sitting outside his wooden shack, the jungle heat oppressing every pore, Aliong wondered whether it was time to leave this place, where the fruit of an African palm had failed to make his fortune. An orange beast, he said, had cursed the family.
“Is this a fair world,” he said, “in which my son’s life is worth less than an orangutan’s?”
Dateline is an award-winning Australian, international documentary series airing for over 40 years. Each week Dateline scours the globe to bring you a world of daring stories. Read more about Dateline
Have a story or comment? Contact Us

